waddell compression test|waddell sign positive test : distributors Waddell’s sign was first described by Professor Gordon Waddell to identify patients who are likely to have poor prognosis following low back pain surgery. But it has been misused and misinterpreted, clinically and medico-legally as a test of credibility and to detect malingering. Many assessors misuse the Waddell’s sign to . See more Assista vídeos pornô de Escola de graça, aqui no Pornhub.com. Descubra a crescente coleção de vídeos e filmes Mais relevantes explícitos em alta qualidade. Nenhum outro .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB3 dias atrás · Le Consultant est une série de Tony Basgallop. Synopsis : À la suite d'une épouvantable tragédie survenue dans les locaux de CompWare, un studio de jeux-vidéo situé en.
waddell's distraction test results
Waddell’s sign was first described by Professor Gordon Waddell to identify patients who are likely to have poor prognosis following low back pain surgery. But it has been misused and misinterpreted, clinically and medico-legally as a test of credibility and to detect malingering. Many assessors misuse the Waddell’s sign to . See moreWaddell signs include: 1. Superficial tenderness: Tenderness over a wide area of lumbar skin to light touch or pinch. 2. Non-anatomic . See moreRotation should be avoided in patients with hip pathologies, as acetabular tear. Axial loading should not be performed in patients with severe neck or cervical spine injury. See moreWaddell’s sign should be done as a part of physical examination in lumbar back pain as it offers only an alert that the patient may need a psychological examination. See more
A systematic review performed by Fishbain et al, concluded that Waddell signs do not identify psychogenic pain nor does it differentiate organic from non-organic problems. A cross sectional study by Adri T et al, assessing the validity of Waddell score stated . See moreWaddell, et al. (1980) described five categories of signs: • Tenderness tests: superficial and diffuse tenderness and/or nonanatomic tenderness• Simulation tests: these are based on movements which produce pain, without actually causing that movement, such as axial loading and pain on simulated rotation
rock hardness scratch test kit
Describe the indications for Waddel sign. Recall the contraindications for eliciting Waddel sign. Summarize the clinical relevance of Waddel sign. Review the importance of improving care coordination among interprofessional team members to improve outcomes for patients affected by low back pain. Waddell (touch-me-not) signs are a set of tests for nonorganicity in low back pain (Video). (1-3) The Waddell signs include a discrepancy between the positivity of straight leg raising between the supine and seated position; pain in the back on pressing down on top of the head; widespread and excessive tenderness (the “touch-me-not” sign . Waddell Signs or Waddell Nonorganic Signs are group of eight clinical physical signs to detect psychogenic, or “non-organic,” low back pain in patients.This test is classically performed with the patient lying in the supine position. The examiner places a hand under the patient's heel and lifts the fully extended leg until pain is reported or.
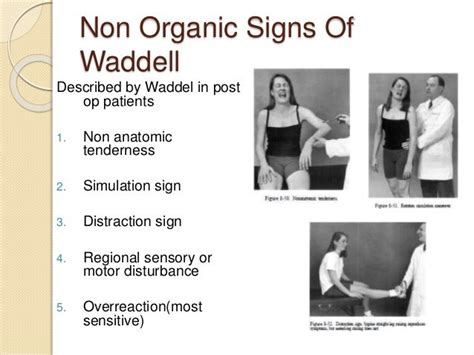
The Waddell sign is a physical examination maneuver used to assess the presence of non-organic or psychogenic signs of pain. It helps healthcare professionals evaluate the potential contribution of psychological or emotional factors to a patient's reported pain. Waddell identified 5 exam findings that correlated with non-organic low back pain
Waddell and colleagues 4 have cautioned medical personnel repeatedly about the hazards of overinterpreting the significance of the signs that bear his name; they state that “Isolated signs .See Article, p 639. In 1980, Waddell et al 1 published a watershed article on the potential contribution of “nonorganic physical signs of low back pain (LBP)” for assessing and understanding this general diagnosis. They described 8 clinical . Explore the purpose, clinical interpretation, and significance of the Waddell sign in pain assessment. Learn how healthcare professionals utilize this examination maneuver to differentiate between pain with organic and non-organic origins, enhancing the understanding of pain complexity. Waddell signs. Waddell’s signs are a group of eight physical signs, first described by an orthopedic surgeon Waddell et al in 1980 1, to identify patients with chronic low back pain who were likely to experience a poor surgical outcome from lower back surgery 2.More recently, clinicians have utilized Waddell signs to detect psychogenic, sometimes inappropriately .
Waddell (1980) Spine 5:117-25 [PubMed] Images: Related links to external sites (from Bing) These images are a random sampling from a Bing search on the term "Waddells Test."
Waddell (touch-me-not) signs are a set of tests for nonorganicity in low back pain (Video).(1-3) The Waddell signs include a discrepancy between the positivity of straight leg raising between the supine and seated position; pain in the back on pressing down on top of the head; widespread and excessive tenderness (the “touch-me-not” sign); general overreaction .
The Waddell Test is a diagnostic assessment that can be used to evaluate the presence of non-organic or psychogenic signs of low back pain. Here are the steps to perform the Waddell Test: Begin by instructing the patient to sit on a firm surface with their hands resting on their thighs. Instruct the patient to relax and maintain a neutral posture. A positive Spurling test indicates you have nerve root compression. This pain can affect your neck, shoulder, or arms. This pain can affect your neck, shoulder, or arms. It sometimes feels similar .Bending the knee while maintaining hip flexion should relieve the pain, and pressure in the popliteal region should worsen it (popliteal compression test). 11 If placing the knee back in full .
waddell's diagnosis
A positive Waddell’s test does not indicate malingering and should not be over-interpreted. To do so is a misuse of this clinical research and contrary of the views of Professor Waddell himself. Determining the truthfulness and accuracy of a claimant’s reported symptoms has always been an art rather than a science, but perhaps the next set .Mini-lecture on Waddell signs in low back pain by William W. Campbell, MD, MSHA, FAAN, FAANEM. See discussion at www.neurosigns.org, follow on FB @neurosigns.
In 1980, Waddell et al. [1] developed a systematic collection of eight physical signs (widely referred to as Waddell signs) thought to measure non-organic subjective pain complaints centered around the lower back and extremities.These signs, reflective of pain complaints, did not have an organic etiology and were originally proposed to objectively predictwhether a patient . 3) Distraction Test (from table of Scalzitti DA (1) adapted from Waddell et al (2)) A positive physical finding is demonstrated in the routine manner, and this finding is then checked while the patient’s attention is distracted; a nonorganic component may be present if the finding disappears when the patient is distracted.Waddell's Signs of Non-Organic Low back pain . Pregnancy test; Only necessary if concerned for infection, tumor, or rheumatologic cause CBC, UA, ESR (90-98% Sn for infectious etiology) . Only necessary if suspect infection, neoplasm, epidural compression syndromes; Consider for back pain >6-8wks, progressive neurologic deficit, or presence .Although Waddell's signs can detect a non-organic component to pain, they do not exclude an organic cause. A high Waddell score (>3) is indicative only of symptom magnification or possible illness behavior. Often the test has been misused. It does not signify malingering. According to an original article the actual numbers of Waddell's signs are 5:
True, Waddell signs have created a lot of problems in the courts, but that does not mean that the competent clinician cannot rise above those abuses and show they are capable of evidence-based medicine. It is equally true that other signs are abused and misused. Many clinicians claim to be able to detect “muscle spasm.” - Terminology used in spine disc pathology and back pain - Differential diagnosis of low back pain - Risk factors for osteoporosis - Solitary nerve root lesions of the lumbosacral spine - Neurogenic vs vascular claudication - Manifestations of OA - Nonorganic low back pain signs (Waddell) - ACP Best Practice Advice - Lower back pain - Cancer tests for back pain
e prospectively evaluated the association between Waddell signs and treatment outcome in 3 cohorts: epidural steroid injections (ESI) for leg pain and sacroiliac joint (SIJ) injections and facet interventions for LBP. Categories of Waddell signs included nonanatomic tenderness, pain during sham stimulation, discrepancy in physical examination, overreaction, .
The Lasegue sign or straight leg raise (SLR) test is a clinical test to assess nerve root irritation in the lumbosacral area.[1] This test is an integral part of the neurological examination of the patients presenting with low back pain with or without radicular symptoms. The other less commonly used name is the Lazarevic sign (see Image. Lasegue Sign). The most useful test involves Straight Leg Raising (SLR). When the patient complains of pain doing SLR while supine but does not complain of pain doing SLR while sitting, the test is positive. This test is commonly referred to as the "flip test."
A doctor may perform a straight leg raise test to determine if the cause of a patient's lower back or leg pain is the result of nerve root irritation or impairment in disc pathology.In a study of 20 hypotheses about the Waddell score in LBP that were then tested in a sample of 229 cLBP patients at a single outpatient rehabilitation center, it was found that the Waddell score . In 1979, the Volvo Award in Clinical Science went to Dr. Gordon Waddell, for his research documented in the following article: Nonorganic Physical Signs in Low Back Pain, by Waddell et al. To summarize, Dr. Waddell identified 5 characteristics of patients exhibiting Nonorganic Physical signs of Low Back Pain. 1. Tenderness.
waddell sign test results
TABLE 18-4 Waddell’s Signs TEST SIGNS From Karas R, McIntosh G, Hall H, et al. The relationship between nonorganic signs and centralization of symptoms in the prediction of the return to work for patients with low back pain. Phys Ther 1997;77:356. Reprinted with permission of the American Physical Therapy Association.
Waddell’s signs. Although most back pain is organic, some patients present with complaints of low back pain that are manifestations of a psychosomatic disorder or for secondary gain. To distinguish behavioral (nonorganic) from organic back pain, Waddell and colleagues found eight signs that identify nonorganic back pain. . Mankopf’s test .
Purpose ‘Low back pain’ (LBP) is a prevalent condition with a majority showing no specific organic pathology. Distinguishing ‘secondary gain motives (SGM)’ from organic causes is imperative in clinical practice. We describe here, three new tests—resistive straight leg raise test (rSLRT), resistive forward bend test (rFBT) and heel compression test (HCT) to help . The Waddell test for tenderness falls into one of five categories. tests for stimulation. . Purpose Technique A few general points to keep in mind while taking the test Positive Test Upper Limb Tension Test 1 (ULTT1, which measures compression of the Median Nerve) is as follows: Upper Limb Tension Test 2A (ULTT2A) Upper Limb Tension Test 2B .
waddell sign test contraindications

Notícias do Corinthians, próximos jogos e resultados do Corinthians. Você encontra tudo sobre o Corinthians no Meu Timão.
waddell compression test|waddell sign positive test